Gases Exam 1 and Problem Solutions
Gases Exam 1 and Problem Solutions
1. Which ones of the followings are true according to kinetic theory of gases;
I. Speed of gas particles are equal under same temperature.
II. Repulsion or attraction forces between gas molecules are too small that they can be neglected
III. Increasing temperature increases average kinetic energy of gases.
Solution:
I. Speed of gas particles is inversely proportional to mass of gas and directly proportional to temperature. Thus, speed of all gas particles are not equal to each other. I is false.
II. Since there are large amount of spaces between gas particles, repulsion or attraction force between them is too small and they can be neglected.II is true.
III. Average kinetic energies of gases are directly proportional to temperature. III is true.
2. System given below is filled with X liquid under 0 0C and 70 cm Hg atmospheric pressure. If density of X is smaller than Hg and tube has cross section area 1 cm2, find which one of the following statements are true for this system.
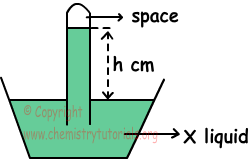
I. h> 70 cm
II. If we use tube having cross section area 2 cm2, h value changes.
III. If we put this system in to sea level, h increases.
Solution:
I. Atmospheric pressure is;
hcm.X=70 cm Hg
H and density of liquid in tube is inversely proportional to each other. So;
dX < dHg and h>70cm Hg, I is true.
II. Cross section are of tube does not affect h value. II is false.
III. Atmospheric pressure at sea level is 76 cm Hg, so pressure of system increases and h also increases. III is true.
3. Which one of the following conditions make gas behave like ideal gas.

Solution:
Gases behave like ideal gas when their temperatures increase and pressures decrease. In given gases, 300 0C is the highest temperature and smallest pressure is 1 atm. II behaves like ideal gas with respect to other conditions.
4. Which ones of the following statements are true related to average molecule speeds of H2 and N2 gases?
I. N2(g) at 40 0C is slower than H2(g) at 40 0C
II. H2(g) at 80 0C is slower than N2(g) at 40 0C
III. N2(g) at 80 0C is faster than N2(g) at 40 0C
Solution: Molar mass of H2 is 2 g/mol and molar mass of N2 is 28 g/mol.
I. At same temperature, molecular speed is inversely proportional to square root of molar masses. Since molar mass of N2 is larger than H2, speed of N2 molecules are slower than speed of H2 molecules. I is true.
II. Average molecular speed is directly proportional to square root of temperature. Since temperature of H2 is higher than N2 and molar mass of H2 is smaller than N2, molecular speed of H2 molecules are larger than molecular speed of N2 molecules. II is false.
III. Since molecular speed is directly proportional to temperature, N2 at 80 0C has larger molecular speed than N2 at 40 0C. III is true.
5. Find value of 0,5 atm in terms of cm Hg.
Solution:
We know that there is a relation between atm and cm Hg;
1 atm = 76 cm Hg =760 mm Hg
1 atm is 76 cm Hg
0,5 atm is ? cm Hg
¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯¯
?=38 cm Hg